| 1 |
a |
a |
a |
Wentzl - a noble, patrician,
merchant and banking family |
|
| 2 |
b |
b |
b |
Uwaga :Powyższa informacja w polskiej wersji
językowej znajduje się tutaj |
|
| 3 |
c |
c |
c |
The
Wentzl’s (derived from Vencelík or Wentzelickh (meaning descended
from Wenceslaus or in Czech Václav), other derivations
include Wentzel, Wentz’l, Wenzlick, Wanclik) and their relations played distinguished
parts in commercial, banking, academic, literary and
other affairs. Their descendants and heirs are alive and well today. |
|
| 4 |
d |
d |
d |
|
|
| 5 |
e |
e |
e |
The Polish Wentzl
Family is a branch of an old Bohemian family of wealthy nobles,
mine owners, merchants and bankers, the Venceliks, humanists and
generous donors of fine arts during the Renaissance period and subsequently. |
|
| 6 |
f |
f |
f |
|
|
| 7 |
g |
g |
g |
The
first records concerning the Vencelik barons of Vrchoviště, kin of the
Smíšek family (see below), with whom they also shared the basic heraldic
symbol in their coat-of-arms - the charge of a white unicorn in an azure
field - date to the era of the last Přemyslid Kings of Bohemia. The
family came to the Kutné Mountains region with its flourishing silver mining
industry (see Kutná Hora) and soon members of the family became Masters
of the Imperial Mint (and managers of their own silver mines). Václav
Vencelík bought Žirovnice Castle in 1485, and subsequently the
family reconstructed it significantly. In 1492, Václav Vencelík and
his brothers Michal and Jan II. Knap obtained the status of
'říšských pánů' (Barons of the Holy Roman Empire, styled
Reichsfreiherr von Sarabitz ze Sarabie) from Holy Roman
Emperor Friedrich III. Vaclav died in Třešť in 1515, but
was buried in Žirovnice. Other properties in Bohemia that once
belonged to the Venceliks included Nová
Včelnice and Stráž nad Nežárkou. |
|
| 8 |
h |
h |
h |
|
|
| 9 |
i |
i |
i |
Václav Vencelík of Vrchoviště had two brothers,
Jan Smíšek (died c.1497) (progenitor of the Smíšek
z Vrchoviště family, a wealthy ore and copper merchant, owner
of mines, owner of Hrádek (now the Czech Museum of Silver and
Silver Mining) and several urban houses in Kutna Hora) and Michal (1483
- 1511) (progenitor of the Libenicky z Vrchoviště
family, Hofmeister of Kutná Hora and also an owner of Hrádek).
See here the beautiful Smíšek Gradual, commissioned and owned
by Michal Smíšek and now in the Austrian National Library in
Vienna. Another branch of this family is the Wentzl
or Wentzel von Sternbach zum Stock und Luttach Family. |
|
| 10 |
j |
j |
j |
|
|
| 11 |
k |
k |
k |
In 1545
the Malovec Family became masters of Kamnice nad Lipou, which they
held for 76 years. Under their rule the Chateau was
reconstructed (mainly in 1580-1583). In 1610 Zikmund
Matěj Vencelík of Vrchoviště, the Commissioner of the
Bechyně Region, became the demesne owner through his marriage with
Anna Magdalena Malovcová. He took part in the Uprising of the
Estates against Ferdinand II. All of his property was confiscated
in 1622. |
|
| 12 |
l |
l |
l |
|
|
| 13 |
m |
m |
m |
In
1490, Václav Vencelík of Vrchoviště
(Virchowitz) bought the Castle of Třešť (German:
Triesch) from Zdeněk Šternberk of Šternberk (Sternberg), together
with Třešť village, the adjoining demesne and the villages
of Jezdovice and Buková as a gift for his son, Matěj
Vencelík of Vrchoviště. The Vencelík Barons of
Vrchoviště and Sarabitz owned Třešť from 1490 to 1626,
when those that supported the Protestant creed had their
property confiscated (the last owner of the estate fought on the losing
side at the Battle of White Mountain, in consequence some
four-fifths of the nobility of Bohemia were dispossessed and obliged to
emigrate). The last Vencelík / Wentzl to own Třešť
was Kryštof Adam Vencelík z Vrchovišt a na Třešťi (d.1626),
married to Regina Dietrichstein (1 voto Herberstein) (d.1630),
whose great-grandmother was Barbara von Rottal (1500 - 1550),
illegitimate daughter of Emperor Maximilian I(1486 - 1519), wife
of Sigmund von Dietrichstein auf Hollenburg (1484 - 1533), whom the
Emperor was said to have favoured as a son. Their wedding was
celebrated in July 1515 in Vienna in the presence of the
Emperor. In the 16th Century the Vencelík Family founded the
Lutheran church of sv. Kateřiny Sienské in Třešť,
where may be found the tombs of Jan Václav Vencelík and of Regina
z Ditrichštejna. |
|
| 14 |
n |
n |
n |
|
|
| 15 |
o |
o |
o |
Johann Wenzel
Vencelík von Vrchoviště (died 1606) was known to
have had a collection of the publications of Martin Luther, Melancthon and
other early Reformist thinkers in his library at Třešť. Among
the supporters of reform the Venceliks were considered to be
moderates. |
|
| 16 |
p |
p |
p |
|
|
| 17 |
q |
q |
q |
A more detailed history of the Vencelík Family
and of Třešť under its ownership may be found here. |
|
| 18 |
r |
r |
r |
|
|
| 19 |
s |
s |
s |
The
family re-established itself in Poland. Maksymilian Wentzel (1750 -
1813) (son of Johann) [i] and his wife Tekla Wierzchanowska (1764 -
1841) had four sons, Jan Kanty Wentzl (1784 - 1866), Antoni Wentzl (1785
- 1855), Maciej Szymon Wentzl (1788 - 1868) andJózef
Maciej Wentzl (c.1796 - 1857), and a daughter, Tekla Agnieszka
Barbara Wentzl (1792 - 1866). Tekla Wentzl married Jan
Chrzciciel Stummer (Sztummer) (1784 - 1845) (admitted to the Mazovian
nobility with crest/herb: Radzisław), Chief Medical Officer of the
Polish Army, President of the Medical Council of the Kingdom of Poland and
holder of the Gold Cross of the Army of the Duchy of Warsaw [ii]. |
|
| 20 |
t |
t |
t |
|
|
| 21 |
u |
u |
u |
Jan Kanty Wentzl (Jan Kanty Wentzel) (1784 - 1866),
was a merchant and restauranteur trading under the name “J. Wentzl”.
Following his marriage to Marianna Haller (1796 – 1880), daughter of Balcer
(Balthazar) Haller, Jan Wentzl and his wife acquired from the Haller Family
the mansion Pod Obrazem at 19 Rynek Główny (the Great
Square)[iii], on the ground floor of which he
operated his restaurant, founded in 1792. This
restaurant operated there under the name “Restauracja Pod Obrazem”
(Restaurant Beneath the Painting), with the family living above, until after
the death of Anna z Wentzlów Laskowska in 1936, becoming among the
best known in Kraków. In 1826 Jan Wentzl is also shown as the tenant
of five shops and three cellars in the building at number 35
Rynek Główny (known as "Krzysztofory"). The
Hallers were a wealthy merchant and patrician Kraków family (descended
from Jan (Johann) Haller (1463 - 1525), a merchant and one of the
first commercial printers in Poland, whose publishing house printed c. 250
publications from 1505 to 1525, including the works of Erasmus of Rotterdam
and Nicholas Copernicus) [iii]. Other notable members of
the Haller family included Lt. General Józef Haller von
Hallenburg (1873 - 1960) and General Stanisław
Haller (1872 –1940), Chief of the General Staff, murdered at Katyn. |
|
| 22 |
v |
v |
v |
|
|
| 23 |
w |
w |
w |
The
mansion at 19 Rynek Główny and its business affairs including the
restaurant were passed down from Jan Wentzl through his son Konrad
Wentzl (1820 – 1897), who married Józefa Brzeska (1833 – 1901), via Konrad’s
sons Ignacy Karol Wentzl (1866 – 1926) (arespected Architect,
whose son Maciej (1903 - 1924) died prematurely) and Maciej Marian
Wentzl (1870 – 1932) to their sister, Anna Laskowska, nee Wentzl (1884 –
1936), who was married to Franciszek Laskowski, but without issue. They
lived mainly separate lives, Anna in Krakow, her husband at his country
estate. |
|
| 24 |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
| 25 |
y |
y |
y |
Under her Testament Anna Wentzl (Anna z
Wentzlów Laskowska) [v] established The Family Foundation of the Wentzl
Families (Polish: Fundacja Familijna Rodziny Wentzlów), bequeathing the
mansion at Rynek Główny and the business of J. Wentzl to the Family
Foundation [vi]. The Testament expressly required that the house be held by
the Family Foundation permanently and that under no circumstances should it
be sold. |
|
| 26 |
z |
z |
z |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Under
the Testament of Anna Wentzl, the object of the Family Foundation is to
use its income to provide material benefits to the descendants of Anna’s
cousin, Maria Waleria z Wentzlów Moczarska (1854 – 1937) and her husband
Ludwik Moczarski (1831 – 1901), to the descendants of Mr Józef
Rostafiński and to the descendants of Mr Józef Stummer, in each case
until the line is fully extinct. The named children of Ludwik Moczarski and
Maria Waleria z Wentzlów Moczarska were: Professor Zygmunt Adolf
Moczarski, Maria Waleria z Moczarskich Zawadzka (vel Zawodska), Helena z
Moczarskich Około-Kułak and Wanda z Moczarskich Peszke. From
these lines there are descendants alive today, each within the class of
beneficiaries of The Family Foundation of the Wentzl Family, all descended
from the Wentzl Family. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Family members who belong to
the class of beneficiaries of the Fundacja Familijna Rodziny Wentzlów
under the Testament of Anna z Wentzlów Laskowska can contact the
law office "Gajek i Wspólnicy. Adwokaci i radcowie prawni sp. k."
in Warsaw for more information and support. You will find all contact
details on the law office's website at: www.mgiw.pl |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
For many years, we have
taken action to create the Foundation and have the opportunity to
pursue the will of our cousin, and also the donor of the Foundation's assets
- Anna z Wentzlów Laskowska. We are very proud of our connections
with the Wentzl family, the home of the Wentzl family and Krakow. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
In
the event of extinction of the families entitled to receive benefits, Anna
directed that the income of the Family Foundation should be used for the
assistance of older ladies of Roman Catholic religion, from good families,
who find themselves either temporarily or permanently in straitened financial
circumstances. Provision was also made for the maintenance of the house. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
The
Testament appointed as the first Board of Trustees Anna’s husband, Franciszek
Laskowski, Dr Antoni Mazanek, her lawyer and Executor of her Testament, and
Jerzy Władysław Zawodski, who died in Buchenwald in 1942
(married to Sabina Maria Jaxa-Marcinkowska h. Gryf (1905 - 1973)). He
was the son of Franciszek Zawodski (1873 - 1956) and Maria Waleria z
Moczarskich Zawodska (1877 - 1961) and the father of Hanna Sabina z
Zawodskich Szamotulska, (1941 -), married to Wojciech Szamotulski (1943 -),
mother of Maciej Jerzy Szamotulski (1976 -) and Marcin Wojciech Szamotulski
(1979 -). Anna directed that future Trustees should be chosen from
among worthy respected people giving an assurance that they will work in the
direction outlined by her Testament. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
The family was not involved in
the selection or appointment of the current Board of Trustees of our Family
Foundation nor with the occupiers of the building at 19 Rynek
Główny or in their arrangements with the Foundation. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
By
her Testament Anna entreated that each Board of Trustees should arrange
that on the Feast of Corpus Christi, on the First Sunday after Corpus
Christi, on the Octave, and on the Feast of Our Lady of the Rosary (the
procession takes place four times a year) for all time in remembrance of her
Family, they should erect an altar on the days when the Church arranges
processions on the Kraków Rynek, as had been the custom of the Family. Anna
declared that all of the decorations of the altar were her property and
bequeathed it to the Family Foundation. She stated that they comprised of
wooden parts, steps, frames, boards, a table, altar frames, a crimson
curtain, 4 matching cloth rosettes, a large carpet, garnish for the frames
(three pieces) in scarlet, 6 wooden candlesticks, a painting representing the
Head of Christ the Lord (always hung on a rope), two milky cases, 4
candelabra, a linen tablecloth, a napkin for the Tabernacle, candle holders
and a candle extinguisher. She said that the Tabernacle is always borrowed
from the Church of St. Mark. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
After
the death of Anna Wentzl her executors sold various items from the house,
including the stone fireplace, which was acquired by the Jagiellonian
University in Krakow for its Senate House. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Due
to the intervention of World War II, Post War Soviet Occupation and Communism
and the consequent political and legal environment in Poland, the Family
Foundation of the Wentzl Family and its ownership of the mansion at 19 Rynek
Główny was not formally confirmed by the Polish Courts until 16 October
1998 [vii]. In this mansion, which is owned by the Family Foundation of the
Wentzl Family, there are now operated a hotel, a restaurant and a cafeteria
under the name Wentzl [viii]: |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Hotel Wentzl - http://www.hotelwentzl.com/en |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Restauracja Wentzl
- http://restauracjawentzl.com.pl/en/ |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Słodki Wentzl - http://slodkiwentzl.pl/en/ |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
In 1935 Anna z Wentzlów
Laskowska and Franciszek Laskowski endowed the National Museum in Kraków
(Polish: Muzeum Narodowe w Krakowie) with the large legacy of Anna’s
brother Maciej Wentzl, which included glassware, ceramics, jewelry (with some
patriotic pieces), timepieces and snuffboxes [ix]. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Józef Tomasz
Rostafinski (crest/herb: Jastrzębiec) was a well known
Botanist, Professor of The Jagiellonian University of Krakow and author of
"Przewodnik do oznaczania roślin w Polsce dziko
rosnących" ("Guide to the Wild Plants of Poland") - of
which there were 21 editions from 1886 to 1979 - and originator of the
"Rostafinski Method" of plant classification [x]. He was the father
of Jan Rostafinski(1882 - 1966), Agronomist and Zoologist, Professor of
The Warsaw University of Life Sciences (SGGW), and grandfather
of Wojciech Rostafinski (1921 - 2002), decorated Home Army (AK)
soldier, participant in the 1944 Warsaw Uprising (codename
"Maslowski"), who later emigrated to the USA and became a NASA
scientist, an engineer and author [xi]. His name is in the
Avenue of Honour in the space exploration Space Walk of Fame. He
was married (in 1949) to Maria Sikorska. The son of Wojciech
Rostafiński, Tomasz Jan Rostafiński, is a doctor of psychology in
Chicago, where, apart from scientific work, he is involved with the
Polish radio station. He has two daughters, Karolina
Rostafiński-Merk and Anna Rostafiński. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Maksymilian Wentzl’s second
son, Antoni Wentzl (1785 – 1855), who married Karolina Zychoniowa (1792
- 1850), was a Head of Department (Naczelnik Wydziału) at The Bank of
Poland (Polish: Bank Polski), as was their son Amilkar Wentzl (1813 - 1881).
They also had a second son, Jan Wentzl (1825 - 1867) and two daughters,
Aniela Wentzl (1810 - 1890) and Karolina Wentzl (1826 - 1896) [xii]. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Maksymilian’s
third son, Maciej Szymon Wentzl (1788 - 1868), was highly trained in
commerce and enjoyed travel and adventure, even once being enslaved by
Turkish pirates. He later became a long serving Director of The Bank of
Poland (from 1840 – 1865) [xiii - xv] and was awarded the Order of
St Stanislaus II Class. In 1845 Maciej Wentzl and his descendants were
admitted as members of the Mazovian Nobility (with the crest/herb: Zbroja)
[xvi]. Maciej married Maria Zuzanna Bayer (Bajer) (1795 - 1876),
daughter of Franciszek Bayer and Justyna Morbitzer, members of prominent
merchant families (Antoni Morbitzer was President of the Krakow Municipal
Council (1812 - 1815, the final years of the Duchy of Warsaw) - overseeing a
significant investment program in the development of the City, its efficient
functioning and modernisation and development as a trading centre, against a
backdrop of Napoleon's war with Russia in 1812 and two year's of Russian
occupation; he was supported in this by Konrad Wentzl). Together they had a
son Adolf (Adolphe) Maciej Bayer Wentz’l (1819 - 1892) and two
daughters, Wilhelmina Justyna Tekla Wentzl (1818 - 1908), who
married Michał Rostafiński (1807 - 1881), a Director of The
Bank of Poland from 1865 – 1874 [xvii], and Berta Wentzl (1828 - 1907). |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Adolf Wentz’l
belonged as a young man to an underground Polish patriotic organisation. He
was sent by the family to his Mother's brother, Julian Bayer (1806 -
1873), in Trieste, where he worked in his uncle's firm, learning English and
Italian (he also knew French, German, Greek, Latin, Polish and
Russian) (Julian Bayer was also an employee of the Bank of Poland and later a
Professor in Warsaw). When the Bank of Poland wanted to establish its
Mint in London he was offered the post of Manager there. As the Manager of
the Mint he made arrangements on behalf of the Bank with London
Zinc Mills for minting coinage. It was while living in England that (on
17 November 1849) Adolf Wentz’l married a widowed Protestant English
lady, Anna Maria Hewlins (primo voto Eachus, widow of Dr. George Eades
Eachus, a Surgeon, composer and violinist), from Emsworth in Hampshire
[xviii]. Adolf became stepfather to Anna's three young children.
The eldest daughter, Mary Eachus, died young, but her son, George
Eachus, became an outstanding engineer, living in Enfield. Anna Eachus,
Anna's younger daughter, remained with her Mother and died in Warsaw in
1920. When the Mint closed, Adolf Wentz'l, renowned for his
integrity, became the London agent of the trading house of Baron Anton
Fraenkel, the financier and founder of Credit Foncier.
Adolf Wentz’l and his family later moved to Paris, where he became
the Private Secretary to Baron Fraenkel for a time, before retiring and
returning to Poland, where he bought an estate near Blonie, Krasnicza
Wola (40 wolki; about 420 acres)(near Grodzisk Mazowiecki), near to his
sister Wilhelmina, married to Michał Rostafiński, at Kludno.
On returning to Poland the family first lived in an apartment in the
house of Maksymilian Fajans, on Krakowskie Przedmiescie, at that time
one of the few houses in Warsaw with mains drainage. Fajans was a
photographer who was constantly trying to improve his art. He had just
started to enlarge photographs and asked for permission to take pictures of
Mr and Mrs Wentz'l and their beautiful, newly married, daughter Maria Waleria
Moczarska (shown here). |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Adolf and
Anna had three children. Adolf (Adolphe) Maciej Bayer Wentzl II (1852 -
1892), who married Maria Plebańska (no issue), Thaddeus (died aged 6)
and a daughter, Maria Waleria Wentzl (1854 -1937), who married Ludwik Antoni
Moczarski vel Mocarski (1831 - 1901) [xix] in Dresden in 1873. They had
first met in London, where he had been sent by The Bank of Poland, for which
he worked. The very talented Adolf Maciej Bayer Wentz'l studied
Engineering, first in England, then in Germany. In an unfortunate
accident he was injured while testing a new engine. Despite two years
of careful medical treatment, his health was ruined. He changed to
Agriculture, completing his studies at the University of Halle, Germany.
He was a keen naturalist (after his death his skilfully mounted
collections of insects were donated to the Jagiellonian University and to the
Academy of Science, his telescope and microscope to the University). He
also managed the estate at Krasnicza Wola to a high level, selecting and
improving the breed of cattle, which became famous in the region, calves and
heifers much sought after. English and French were the main languages
of the house. Zygmunt Moczarski spent much of his upbringing here,
until the successive double loss of his beloved Grandfather and Uncle, when,
affected by these losses, he chose not to look after the estate and it was
sold, which he later regretted. Adolf Maciej II died aged 40 in 1892 from
Typhus, contracted through tending to others who had contracted this disease.
After her husband's death, his widow, Maria Wentz'l worked as a
secretary in the Warsaw Library and also translated books - in 1899 H.G.
Well's influential science fiction novel "The War of The
Worlds" (first edition in 1898) was first published in Poland,
translated into Polish by Maria Wentz'l (nee Plebańska)
Maria Plebańska, was the eldest daughter of Prof.
J.K. Plebański, former professor at the Central Academy (Szkola
Glowna), a historian, who lived at Izdebno, inherited by his wife from the
Skorzewski family. Clementina Tanski-Hoffman (authoress) was brought up
at Izdebno. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Ludwik
Moczarski was the third son of Antoni Moczarski (1787 - 1867) and Franciszka
Zawadzka. Antoni Moczarski's parents were Jan z Mocar Moczarski vel
Mocarski (1716 - c. 1790) (crest/herb: Łada) [xx] and his
third wife Anna Supińska. Jan was hereditary owner ofMocarze [xxi]
the estate comprised of Mocarze Budne, Mocarze Dziubiełe, Mocarze
Starawies, Bartki and Zabłotne, adjacent villages, in the parish of
Burzyn near the Biebrza Marshes in Łomża County, c.50km
North-East of Warsaw. Some 1200 acres were purchased in 1435 by
two brothers, Maciej and Jan Moczarski, as confirmed in a patent by
Wladysław, Prince of Mazovia. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
This
old Mazovian noble family is descended from Piotr Pilcha / Pilch /
Pelko, Castellan of Czersk (1224) (the main administrative centre
of the Duchy of Czersk - before Warsaw the seat of the Piast
Family, ruling Dukes of Mazovia), a confidant of Prince Konrad of Mazovia and
a member of a then widely known noble family (whose crest
was Jastrzębiec - "jastrząb" means
"goshawk", one of the oldest Polish crests / noble clans, whose
ancestor in 998 was accorded by King Boleslaw the
Brave the addition of a horseshoe to his crest in honour of a
successful recorded act of valour). For his impressive victory against
the Jadzwings (Prussians) in about 1220, Piotr Pilch was given the
village Łada and became the first to be given the crest / herb
Łada, taking Łada as his family name. From his
son Wladysław Łada, Commander of the Army of Mazovia,
also came Mikołaj [Nicholas] Moczarski vel
Mocarski (c.1590 - 1638), the last Colonel of the Lisowszcycy –
“The Horsemen of the Apocalypse” [xxii] (and see the
enigmatic "The Polish Rider" attributed to Rembrandt, a
Lisowczyk?). |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
“In the burnt-down church of Barefoot Carmelites
[the fire occurred in 1803], there was a black marble gravestone to
Mikołaj Łada Mocarski, colonel of the Lisowczycy.” Those words can
be read in „Obraz Miasta Lublina” (A Picture of the City of Lublin),
published in 1839. The text of the Latin inscription was noted by Szymon
Starowolski (1588 – 1656), a priest and a writer: "The noble knight of
old blood, the famous Sir Mikołaj of Mocar Mocarski, son of Ziemia Wiska
[medieval north-eastern Mazovia], chevalier of the Łada crest. The
Commander of mounted troops of His Royal Majesty. Thoroughly educated in
Catholic faith, he twice prevailed over the Moskal [Muscovites]. For
Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, he stood against and inflicted pain on his
enemies : Gabriel of Transylvania and Frederick, Electoral Palatine [at The
Battle of White Mountain 1620]. At Chocim, he faced the Ottomans in battle
without fear. In Prussia, he inspired great fear and terror in Gustav, Duke
of Södermanland [later Gustavus II Adolphus of Sweden]. In the
Borderlands of our Patria he stood watch and defended her most fervently. And
when the eyes of all Polish warriors were on him and admired him, death
cold-heartedly found him. He fell to his death pierced by rebelling Kossacks
[in] violent tumult at Kumeyki Village” (translated from Latin by O. A.
Smagacz of the Order of Barefoot Carmelites in Lublin)[xxiii]. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Mikołaj Moczarski received
honourable mention in the historian Simon Starowolski's book
on "Sarmatian Warriors" ("Wojownicy sarmaccy, czyli
pochwały mężów słynących męstwem wojennym w pamięci
naszej lub naszych pradziadów" - containing biographical
information on some 130 Polish and Lithuanian kings and knights), first
published in Latin in the 17th century: "Mikołaj Moczarski,
especially prominent in the art of war, which in our times
still sustains that flourishing branch, beginning bravely in
Prussia. He maintained the fame of Lisowski, winning many actions
against Swedish troops (he later won a series of victories in the
years 1634 - 1636)". |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
PLEASE TURN TO THE CONTINUATION PAGE FOR MORE INFORMATION |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Family Tree |
|
| |
|
|
|
References |
|
| |
|
|
|
Testament (and certified English translation) of
Anna Laskowska (nee Wentzl) - Anna z Wentzlów Laskowska |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
All
rights reserved |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
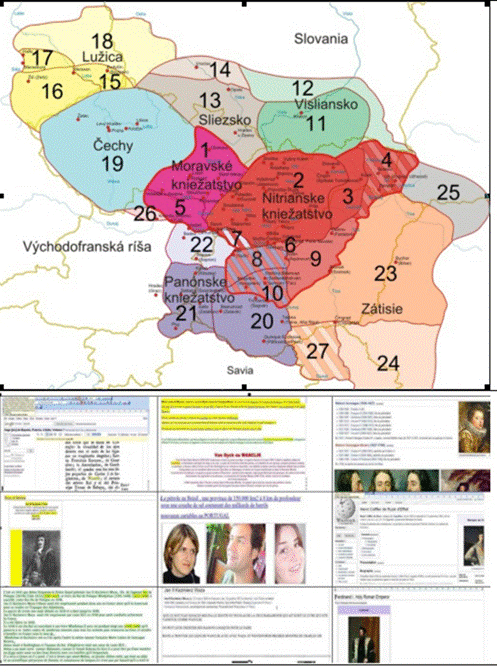
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Vendéliques |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
(Redirigé
depuis Vindélicie) |
|
| |
|
|
|
Aller ŕ : Navigation, rechercher |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Les Vendéliques ou encore Vindélices, Vindéliciens1, en latin Vindelici, Vindolici ou Vindalici, désignent un peuple
habitant une ancienne région romanisée sous le nom de Vindélicie. Elle s'étend entre
le Danube au
nord qui a été sur le limes de Germanie), la Norique ŕ l'est au delŕ de l'Oenus (Inn), la Rhétie premičre au sud et la Gaule ŕ l'ouest qui commence par
l'ancien territoire des Helvčtes. Cela correspond aujourd'hui au territoire comprenant la
partie nord-est de la Suisse, le sud-est de la région de
Bade, et le sud du Wurtemberg et de la Bavičre. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Sommaire |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
[masquer] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
1 Habitants de la
Vindélicie |
|
| |
|
|
|
2 Histoire |
|
| |
|
|
|
3 Sources |
|
| |
|
|
|
4 Notes et références |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Habitants de la Vindélicie[modifier] |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
La Vindélicie primitive
soumise l'an 15 avant J.-C. et protégée par les Romains prend son nom latin
de l'accolement de deux rivičres qui l'encadrent, la Lech et la Wertach, autrefois dénommée Licus et Windo. Notons que Vindo, Winda en latin, provient
d'un mot celte signifiant « blanche ». Les
populations déclarés celtes ou gauloises par les conquérants, mais en réalité
des Sučves dissidents
soutenant en cachette les peuples Rhčtes dans leur farouche résistance ŕ
Rome, se nomment : Licates, Rucciinates, Caténates, Consuanetes... |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Comme les Sučves se doivent
d'ętre l'allié des Romains, cette région est conquise et intégrée de facto ŕ
la province de Rhétie. Les troubles qui éclatent permettent aux légions
victorieuses d'accroître le périmčtre de sécurité au Danube. Les habitants sont
dénommés par commodité Vindéliques. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Le principale citadelle
de Vindélicie est l'oppidum de Manching prčs d'Ingolstadt. Sur ce territoire, une ville est fondée par les légions
romaines de drusus la colonia Augusta
Vindelicorum qui devient l'« Augusta
des Vindélices » ou Augsbourg). Elle est aprčs 90 la plus importante et la plus prospčre de
Rhétie avant que l'empereur Marc-Aurčle l'en sépare, fondant ainsi la Rhétie seconde dans le
diocčse d'Italie. La Rhétie premičre reste alpine, centrée sur Coire. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Si la vieille culture archéologique de la
Vindélicie appartient sans conteste ŕ La
Tčne, les habitants romanisés au IIIe sičcle réinventent
le gentilé Vindelices oublié, conscients que leurs ancętres celto-germaniques
parlaient un langage celtique, alors qu'il fréquente de plus en plus
étroitement le monde germanique. Les érudits étymologistes ont pu noter aussi
que d'autres peuples antiques proches ont un nom apparent : Vandales, Vénčdes, Vénčtes ou Wendes ou encore le camp
romain antique de Vindonissa, aujourd'hui au nord de la Suisse. Mais faut-il préciser que les Vendéliques qui
doivent leur nom aux deux rivičres qui traversent leurs
territoires, sont le produit d'une mythogénčse latine. Toutefois, parmi les
tribus ou régions qui leur sont inféodées, on trouve les Brigantii (dans la
région de Bregenz),
les Estiones (région de Kempten), les Licates (vallée de la Lech) et plus ŕ l'est les
Catenates, les Cosuanetes et les Rucinates, attestant l'importance de la cité
capitale Augusta Vindelicorum et la vieille influence sučve sur ce qui est
aujourd'hui le sud du Wurtemberg et la Bavičre occidentale. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Počiatky rodu sa
podľa Poľskej národnej legendy datujú okolo
roku 960 n.l. kedy bol Skubek povýšený
medzi družiníkov kniežaťa Ziemomysla . Od tej doby sa uvádzal
ako rod Wężyk , ktorý mal svoje rodové sídlo Wola
Wężykowa. Rozrastaním rodu sa vytvorili nové vetvy
, Kostrowicky, Osinsky, Vestersky, Borkovsky, Goriansky, Podolsky ...
Rod sa veľmi rýchlo rozrástol. Smonk v podobe hada, ktorého Skubek
podľa legendy zabil, sa stal rodovým symbolom a neskôr erbom. Na
rozdiel od Germánskej či tzv. západoeurópskej tradície
, kde erb mohol mať v rode každý z bratov iný, mali Poliaci až do
konca 15 storočia erb rodový, ktorý vyjadroval pokrvnú príbuznosť
tak ako v škótsku , či keltskom Írsku. Rod už začiatkom 15
storočia mal priezvisko vyprofilovane a už
aj historicky zaznamenane... Pôvod mena Venžík je evidentne preukázaný
z poľštiny - litovčiny. Jedná sa o fonetický prepis
čítaného slova Wężyk - tak, ako ho počujú tí,
čo nepoznajú správnu výslovnosť (tj. cudzinci,). (pozn.: a =
„on" , e = „oen"- číta sa veľmi krátko „o" sa hltá,
y po ž sa číta mäkko a stredne dlho), Podľa mena
Wąż - Had , číta sa Vonž , Wężyk - z
hada, patriaci hadovi , číta sa Venžík , - patronim pri tvorbe
sufixu v priezviskách v Poľštine. V Poľštine je jeden had -
Wąż a (dva) hadi už sú Węży. Asi hovorovým
spôsobom vzniklo množné číslo Wężyki . Z toho
spätne pre jednotné číslo vzniklo pomenovanie Venžík -
Wężyk . Obdobne aj v Slovenčine sú
koncovkou -ík, -ník, tvorení slová les - lesník a pod. Preto
neskôr nebolo možné ako u iných Poľských rodov k nemu
priradiť cudzích, bez pokrvnej príbuznosti, len podľa podobnosti
mena, lebo ich meno už bolo evidentne vytvorene v dávnej dobe a je
nezameniteľné, takže iné sa na neho ani nepodobalo.
Wężyki sú teda všetci príbuzní a potomkovia SKUBEKA ! |
|
| |
|
|
|
Pôvodná vetva
osídľovala Miechov, Poleje a Osiny v Krakovsku. Rod patrili
medzi Mazovské kniežatá ( ksiac – kniežatko) až do Horodelskej
únie. Vroku 1410 tiahol kráľ WŁADYSŁAW
JAGIEŁŁO a jeho brat VITOŁD -Veliké Knieža Litevské
do vojny proti rádu nemeckých rytierovan. V ich osobnej družine a
stráži bol aj Jan Wężyk z Dąbrowy
ktorý tlmočil z nemeckého jazyka a Mikołaj
Wężyk i Bogufał kuchmistri kráľovský. Príslušníci
rodu boli medzi 47 rodmi pri založení Velikého kniežatstva
Poľko-Litevského, Rzeczipospolitej Obojga Narodow 2.10. 1413 v
Horodle. Od tejto doby sú „prísažné“ rody Horodelskej únie
považované za najvyššiu Poľskú a Litovskú šľachtu, ktorej sú i
tzv. kniežacie (v Poľsku a Litve sa šľachta odvtedy
nedelila na hodnosti) rody povinné preukázať úctu. Iba prísažné rody mohli voliť a byť zvolený za Veľké
Knieža. Venžíci obsadzovali najvyššie funkcie ako Vojvoda Vielopolski,
Vojvoda Koniecpolski, Vojvoda Belsky, Zemský sudca, Veliteľ vojsk,
Hlavný lovčí a pod. Pôsobili aj ako starostovia a kasteláni miest
Vschov, Miechov, Krakov a i. Rodu patrili i hradné sídla Kowale,
Drahimia, Kornik a iné... Potomkovia z vetiev Kostrowicky a
Sulkovsky sa stali Veľkými Kniežatami Litvy a Ambrozievic zasa
Malopoľské a České Knieža a Český princ. Družiníci Goriansky,
z kráľovskej družiny doprevádzajúcej princeznú Annu,
ktorá sa mala vydať za Uhorského kráľa Ladislava I-
Svätého, sa stali významným magnátskym rodom Uhorska. Títo vládli ako Báni
v Slavónii, Sriemsku a Mačve. Z oboch vzniknutých vetiev
Gorianskych sa príslušníci rodu striedali Uhorskými palatínmi, kde
vykonávali faktickú vládu v mene Kráľa nad Uhorskom viac ako 100
rokov. Ich hlavné sídla boli Devín, Budín a Siklos. Patrila im aj
Liptovská župa, Uhrovec a Presburg (Bratislava). Medzi významné
cirkevné osobnosti patril aj Jan Venžík, ktorý sa stal Arcibiskupom
Hniezdenským a Prímasom Poľským, ktorý po smrti kráľa Vladislava
vládol pod interegnum ako de jure Vice Rex , až do zvolenia nového
Kráľa.. Týmto rod dostal výsadu Korunovať kráľov Poľska,
čo sa aj niekoľko krát stalo a obdržal i iné významné
výsady. Ako Prímas Poľský mal aj svetskú hodnosť Kniežat rýše
rýmskej. Z rodu bolo viac biskupov-kniežat a kňazov. No
nielen Duchom, ale hlavne mečom vládli Venžíci. Iný Ján Venžík udelil
ako Vojvoda Podolský zdrvujúcu porážku Tatárom . Ako dôkaz ich
statočnosti svedčí fakt, že piati príslušníci rodu obdržali
najvyššie vojenské vyznamenanie Order Virtutti Militery. Toto
vyznamenanie je považované za jedno z troch najhonosnejších vojenských Radov
na svete, spolu s Victoria Cross a Cross of Glory . Iný boli
držiteľmi Radu Bieleho orla, či Radu Sv. Juraja. Venžíci ako
významní velitelia vojsk sa presadzovali aj mimo Poľsko a
Litvu. O príslušníkoch rodu sú v Poľsku viaceré Národné legendy
opisujúce ich hrdinské činy. V Česku bol Vladika Jiřík
kapitánom Naměšti nad Oslavou, Jan Dionísius
hejtmanom Letovíc , Jaroš zasa rakúskeho Hardegu. Patrili medzi
ochrancov povestnej Biblie Kralickej, ktorá i vďaka
nim sa zachovala dodnes. Náhrobný kameň
Jiříka sa nachádza uložený v Kralickom kostole. Na území
dnešného Slovenska sa uvádzajú už od roku
1540. Stanislav Venžík si okolo roku 1590 zobral za manželku
baronesu Alžbetu Pograny, dcéru Baróna Benedikta Pograny de Nemes
Kürt. Zúčastňoval sa bojov proti Turkom.
Pograny bol vlastníkom a kapitánom hradu Vigľaš a významný
proti Turecký bojovník v hodnosti Zadunajského generála . Svoje dcéry
vydal za najstatočnejších veliteľov svojho vojska, Stanislausa
Venchika a Ladislausa Zay de Cömör. Stanislav Venžík neskôr padol v boji
proti Turkom okolo roku 1595 v bitke o Nové Zámky. Nakoľko sa
sobášom s baronesou Alžbetou Pograny stal zároveň švagrom baróna
Ladislava Zay, jeho potomkov uchýlili Zayovci k sebe na hrad Uhrovec,
ktorý im už v tej dobe patril (Týmto sobášom sa opäť pokrvne stretajú s
vetvou z Gorian) No viac ako o siroty, sa Zay zaujímal hlavne o
ich majetky najmä v Nemes Kürth (Zemianske sady) , hrad Vígľaš a
kaštieľ Jaslovské Bohunice, v ktorých mali ako spoluvlastníci významný
podiel. Akým spôsobom ich Zayovci pripravili o majetok nieje celkom
známe. Pravdepodobne ešte ako majetok sirôt previedli pod svoju správu.
Alžbeta sa vydala po druhý krát za deda posledných
sedmohradských kniežat , Sebastiána Tököly de
Kecsmárk. Od tej doby ďalší Venžíci pôsobili v službách
Zayovcov. Tu zastávali významné hospodárske funkcie. V roku 1659 im
panovník obnovil šľachtický stav pre Uhorsko a celú Sv. Ríšu Rímsku
, opäť za zásluhy v boji proti Turkom. V roku 1675 sú
uvádzní v súpise šľachty Bratislavskej stolice. No ako málo majetný
rod sa nepresadili v žiadnych významných funkciách. Výnimkou je
Gašpar Venchik , ktorý pôsobil okolo roku 1845 ako prísažný
prísediaci Prešporskej stolice. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Sobášmi je rod
pokrvne spriaznený s Uhorskými rodmi Zay de Cömör, Balassa de
Gyarmat, Pograniy de Nemes Kurt, Kohary de Czabrak, Kálnoky de
Kövöszpatak, Dobsa , Pongracz, Vanko, Trebichavský, Babindali, Tököly,
Schura, Kozič, Mlynár, Kušnier . |
|
| |
|
|
|
Po roku 1804
odišli z Uhrovca a usadili sa v Trnave a jej okolí. Tu žijú Venžíci dodnes.
Ján Wenžik bol aj príslušníkom delostreleckej brigády v
Trenčíne, ktorá zohrala významnú úlohu pri vzniku samostatného
Československa po skončení prvej svetovej vojny. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Z iných krajín kde
pôsobili Venžíci je treba pripomenúť významného Francúzskeho poeta
Guilieme Venzik Kostrowicky - Apolinaire, ktorý bol zároveň aj vnukom
Napoleona I. Taktiež Českého učenca a zakladateľa reálneho
Českého školstva Jozefa Wenzika (Wenziga) , ktorý bol aj
učiteľom Žofie Chotkovej, manželky následníka Rakúsko-Uhorského
trónu, ktorých zavraždili v Sarajeve. Jeho najznámejšími sú libretá k
k Smetanovým operám Libuša , Dalibor a iné. Po Jozefovi Wenzigovi je v
centre Prahy pomenovaná ulica. V súčasnosti na internete je možno nájsť Venžíkov po celom svete. Pôsobia od
výpočtového strediska NASA, cez ekológov v Amazonskom pralese, či
ako lekári v Egipte, alebo riadia obchodný koncern v Holandsku či
lodenice v Rusku. Aj Venžíkov ako športovcov v medzinárodných súťažiach
možno nájsť, či študentov univerzít ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
Autor textu: Ladislav Venžík |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžík or
Polish origin Wężyk a Polish family. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Arystokratycznej rodzinie of
Siedziba w Czech, Morawa and |
|
| |
|
|
|
(Być w may Czeska
Królewstwem) |
|
| |
|
|
|
przed
after Biala Gora |
|
| |
|
|
|
Rod wykazano wcześniej
życia |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
File: Venzik.jpg |
|
| |
|
|
|
Crest |
|
| |
|
|
|
The origins of the genus, according to Polish national
legends date back to around 960 |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kr. when he was promoted between Skubek
družiníkov kniežaťaZiemomysla |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
. Since then, as
stated Wężyk family, who had his family seat |
|
| |
|
|
|
Wola Wężykowa. Sprawl
family to create new branches, Kostrowicky, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Osinska, Vestersky,
Borkovský, Goriansky, Podolsky ... Rod is very |
|
| |
|
|
|
quickly expanded. Smonk
in the form of a serpent, which according to legend Skubek |
|
| |
|
|
|
killed,
became a symbol of gender and later arms. Unlike the Germanic |
|
| |
|
|
|
or
so. Western European tradition, where the arms could have rode in
any of |
|
| |
|
|
|
other
brothers, the Poles had until the end of the 15th century ancestral coat
of arms, which |
|
| |
|
|
|
reflect the
affinity of blood as in Scotland, Celtic and Ireland. Genus |
|
| |
|
|
|
early 15th century
was profiled last name and has also historically |
|
| |
|
|
|
recorded
... |
|
| |
|
|
|
Origin of name Venžík
is clearly demonstrated from the Polish - Lithuanian. This |
|
| |
|
|
|
is the phonetic word is
read Wężyk - as you hear those who |
|
| |
|
|
|
know the
correct pronunciation (ie foreigners). (Note: a = "on", e
= |
|
| |
|
|
|
"Oen"
- read the very short "o" devours, y to z is spoken softly and
moderate |
|
| |
|
|
|
long), In the
name of the WAZ - Snake, read the Vonž, Wężyk - the snake,
belonging |
|
| |
|
|
|
serpent, read
the Venžík - patrons to create a suffix on surnames in |
|
| |
|
|
|
Polish. In
Polish it is a snake - and WAZ (two) snakes are already
Węży. About |
|
| |
|
|
|
colloquial manner originated
plural Wężyki. It recovered to |
|
| |
|
|
|
singular term
originated Venžík - Wężyk. Similarly, in |
|
| |
|
|
|
Polish the
suffix-ik,-nik, word forest - and the forester. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Therefore
could not be later than in other Polish families assigned to him |
|
| |
|
|
|
foreign, no
bloodline relationship, only under the name similarity, because their |
|
| |
|
|
|
name has been clearly
established in ancient times and is irreplaceable, so |
|
| |
|
|
|
others not even resemble
him. Wężyki are therefore all the relatives and |
|
| |
|
|
|
Skubeka descendants. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
The original branch settled by
Micah, spill and pain in Krakow. Rod included |
|
| |
|
|
|
between Masovian princes
(ksiac - kniežatko) until Horodelskej Union. |
|
| |
|
|
|
In the period 1410
kráľVladislav Jagiellonian and dragged his brother Vitold -
Lithuanian |
|
| |
|
|
|
archduke to war against the
Teutonic Order. In their personal retinue |
|
| |
|
|
|
a guard was also
Wężyk Jan Dabrowa of which conveyed the German language and |
|
| |
|
|
|
Mikołaj Wężyk i
Bogufał kuchmistri royal. Family members were among |
|
| |
|
|
|
47 genera in establishing the
polka-Lithuanian veľkokniežatstva (Rzeczipospolitej |
|
| |
|
|
|
Obojga Narodowy)
10.02 1413 Horodle. Since then, the "oath" genera |
|
| |
|
|
|
Horodelskej Union considered
the highest Polish and Lithuanian nobility, |
|
| |
|
|
|
which are also
called. prince (in Poland and Lithuania since the nobility
nedelila |
|
| |
|
|
|
on rank) to demonstrate
respect for families. Only sworn and families to
vote |
|
| |
|
|
|
be elected for the
archduke. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci occupied in steps as
the highest function Vielopolski Duke, Duke |
|
| |
|
|
|
Koniecpolski, Duke Belsky,
Regional judge, army commander, and Master hunter |
|
| |
|
|
|
below. Served as mayors
and warden posts ICT, spinal cord, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Krakow and Others Genus also
included the Castle residence Kowal, Drahimia,
Kornik and other ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
Descendants of branches and
Kostrowicky Sulkovsky become great prince |
|
| |
|
|
|
Lithuania and Ambrozievic turn Lesser
Czech and Bohemian prince and prince. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Družiníci Goriansky, the royal
entourage accompanying a princess Anna, |
|
| |
|
|
|
to be issued under King
Ladislaus I of Hungary, Holy, became |
|
| |
|
|
|
significant gender magnate
of Hungary. They ruled as Bani in Slavonia, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Srem and MACV. Arising from both branches are members Gorianskych |
|
| |
|
|
|
family turns Uhorskými
Palatine, where the government carried out practically on behalf of |
|
| |
|
|
|
The king
of Hungary more than 100 years. Their main headquarters were Devin Buda |
|
| |
|
|
|
and Siklos. Belonged to them and Liptovská County, and Uhrovec
Presburg (Bratislava). |
|
| |
|
|
|
Major religious figures
included the Venžík John, who became |
|
| |
|
|
|
Hniezdenským archbishop and
primate of Poland, after the death of King |
|
| |
|
|
|
Vladislav ruled under
interegnum as de jure Vice Rex, until the election |
|
| |
|
|
|
New King .. This family got the privilege of crowning the kings
of Poland, as well as |
|
| |
|
|
|
happened several times and
received and other important privileges. As Primate
of Poland |
|
| |
|
|
|
also had a secular princes
rank Holy Roman Empire. The
family was more |
|
| |
|
|
|
bishops, priests and
princes. But only the Spirit, but mainly ruled by
the sword |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci. Other than John
Venžík gave Duke Podolsky crushing defeat |
|
| |
|
|
|
Tatars. As proof of their
courage demonstrated by the fact that the five members |
|
| |
|
|
|
family received the highest
military decoration Order Virtutti Militery. |
|
| |
|
|
|
This award is considered one
of the three najhonosnejších |
|
| |
|
|
|
Military ranks of the world,
along with the Victoria Cross and Cross of Glory. Other |
|
| |
|
|
|
were in possession of the
White Eagle, and St. Council. George. Venžíci as |
|
| |
|
|
|
prominent commanders of troops
to enforce outside Poland and Lithuania. O |
|
| |
|
|
|
the members of the family are
in Poland several
national legend describing their |
|
| |
|
|
|
heroic deeds. In the Czech Republic was
vladika captain George Namest nad Oslavou |
|
| |
|
|
|
Jan Dionísius captain
Letovice, Jaros Austrian Hardeg again. Included |
|
| |
|
|
|
between the defenders of the
notorious Kralice Bible, which also thanks to them |
|
| |
|
|
|
has been preserved. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
On the territory of Slovakia are listed since 1540. Stanislav
Venžík |
|
| |
|
|
|
to around 1590, took to wife
Elizabeth Pograny baroness, daughter |
|
| |
|
|
|
Baron Benedict Pograny Kürt de
Nemes. He participated in the battles against |
|
| |
|
|
|
Turks. Pograny was the
owner and captain of the castle Vígľaš a significant anti- |
|
| |
|
|
|
Turkish fighter in
Transdanubian rank of general. My daughter went to |
|
| |
|
|
|
najstatočnejších
commanders of his army, and Stanislaus Venchika |
|
| |
|
|
|
Ladislaus de Zay
Comoro. Stanislav Venžík later fell in battle against |
|
| |
|
|
|
Turks around the
year 1595 in the Battle of New Castle. Since the marriage of |
|
| |
|
|
|
Baroness Elizabeth Pograny
while her husband became Baron Ladislaus Zay, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Zayovci his descendants fled
to the castle itself Uhrovec that they had in the |
|
| |
|
|
|
it belongs (this marriage
is once again come together by blood, with a branch of Gorian). |
|
| |
|
|
|
No more than orphans,
Zay is mainly concerned about their property in particular
Nemes |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kurth (Zemianske sets), castle
and manor Vígľaš Bohunice in |
|
| |
|
|
|
which were co-owners as a
significant proportion. How does their |
|
| |
|
|
|
Zayovci prepare the property
is not fully known. Probably more than |
|
| |
|
|
|
orphans property
transferred under its administration. Since then further Venžíci |
|
| |
|
|
|
engaged in services
Zayovcov. There have held important economic functions. |
|
| |
|
|
|
In 1659, the ruler restored
aristocratic status for Hungary and the whole
St. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Rome's empire, once again
merit in the fight against the Turks. In 1675, the uvádzní |
|
| |
|
|
|
in inventory
nobility Bratislava stool. But how few are wealthy family |
|
| |
|
|
|
have failed in any important
positions. The exception is Venchik Gaspar, |
|
| |
|
|
|
who worked around the year
1845 as a sworn juror Prešpor |
|
| |
|
|
|
stool. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Family by blood marriage is
associated to strains from Hungary Zay de Comore, Balassa |
|
| |
|
|
|
de Gyarmati, Pograniy de Kurt
Nemes, Kohar Czabrak de, de Kálnoky |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kövöszpatak, Dobsa, Pongracz,
Vanko, Trebichavský, Babindali, J ", |
|
| |
|
|
|
Schur, the bottles, miller,
Kušnier. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
After 1804, they went from
Uhrovec and settled in Trnava and its surroundings. Living here |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci today. John was
also a member Wenžik artillery brigade |
|
| |
|
|
|
Trencin, which played an
important role in the establishment of the independent Czech and |
|
| |
|
|
|
Slovakia after the First World
War. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
In other countries where the
act is to be noted Venžíci significant |
|
| |
|
|
|
French poet Guile Venzik
Kostrowicky - Apolinaire, which was |
|
| |
|
|
|
also a grandson of Napoleon
I. Also, the Czech scholar and founder |
|
| |
|
|
|
Real Czech Education Joseph
Wenzika (Wenzig), which was also |
|
| |
|
|
|
teachers Chotkova Sophie, wife
of heir the throne of Austria-Hungary, |
|
| |
|
|
|
were killed in Sarajevo. His best known are the libretto for the |
|
| |
|
|
|
Libuša cream again, Dalibor
and others. After Joseph is Wenzig |
|
| |
|
|
|
the center
of Prague named street. Currently, the Internet can find |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíkov worldwide. Operate from the NASA data center, through |
|
| |
|
|
|
environmentalists in the
Amazon, or as doctors in Egipto, or manage |
|
| |
|
|
|
business group in
the Netherlands and Russia in the yard. Even as Venžíkov |
|
| |
|
|
|
athletes in international
competitions can be found, or university students |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Traduction (slovaque >
français) |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžík ou d'origine polonaise Wezyk une famille
polonaise. |
|
| |
|
|
|
rodzinie Arystokratycznej de w Siedziba tchčque, Morawa et |
|
| |
|
|
|
(W
BYC peut Czeska Królewstwem) |
|
| |
|
|
|
przed
aprčs Biala Gora |
|
| |
|
|
|
wykazano Rod wcześniej zycia |
|
| |
|
|
|
Fichier: Venzik.jpg |
|
| |
|
|
|
Crest |
|
| |
|
|
|
Les origines du genre, selon les légendes nationales polonaises remontent ŕ environ
960 |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kr. quand il a été promu entre kniežaťaZiemomysla družiníkov
Skubek |
|
| |
|
|
|
. Depuis lors, que
la famille a déclaré Wezyk, qui avait son sičge famille |
|
| |
|
|
|
Wola
Wężykowa. L'étalement de la famille pour créer de
nouvelles succursales, Kostrowicky, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Osinska, Vestersky,
Borkovsky, Goriansky, Podolsky ... Rod est trčs |
|
| |
|
|
|
rapidement élargi. Smonk
sous la forme d'un serpent, qui selon la légende Skubek |
|
| |
|
|
|
tué, est devenu un symbole
du sexe et des armes plus tard. Contrairement ŕ la germanique |
|
| |
|
|
|
ou alors. Western
tradition européenne, oů les armes pourrait avoir roulé dans l'un
des |
|
| |
|
|
|
autres frčres, les
Polonais avaient jusqu'ŕ la fin de la robe du 15čme sičcle ancestrales
des armes, qui |
|
| |
|
|
|
reflčte l'affinité du
sang comme en Ecosse, le Celtic et l'Irlande. Genre |
|
| |
|
|
|
début du 15e sičcle a
été profilée nom de famille et a également passé |
|
| |
|
|
|
enregistrés ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
Origine du nom Venžík
est clairement démontrée de la Pologne - Lituanie. Cette |
|
| |
|
|
|
est le mot phonétique est
lu Wezyk - que vous entendez ceux qui |
|
| |
|
|
|
connaître la
prononciation correcte (ŕ savoir les étrangers). (Note: un e =
"on", = |
|
| |
|
|
|
"Oen" - lire le trčs
court "o" dévore, y ŕ z est parlé doucement et modérée |
|
| |
|
|
|
long), Au nom de la WAZ
- Snake, lire le Vonž, Wezyk - le serpent, appartenant |
|
| |
|
|
|
serpent, lire le Venžík -
au public de créer un suffixe des noms de famille dans |
|
| |
|
|
|
Polonais. En polonais, il
est un serpent - et WAZ (deux) serpents sont déjŕ Węży. A
propos |
|
| |
|
|
|
maničre familičre origine du
pluriel Wężyki. Il s'est rétabli ŕ |
|
| |
|
|
|
terme singulier origine Venžík
- Wezyk. De męme, dans |
|
| |
|
|
|
Polonais le suffixe-ik,-nik,
foręt mot - et le forestier. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Par conséquent ne pouvait pas
ętre plus tard dans d'autres familles polonaises qui lui sont assignées |
|
| |
|
|
|
étrangers, aucune relation
lignée, que sous le nom de la similitude, parce que leur |
|
| |
|
|
|
le nom a été clairement
établie dans l'Antiquité et est irremplaçable, de sorte |
|
| |
|
|
|
d'autres męme pas lui
ressembler. Wężyki sont donc tous les parents et |
|
| |
|
|
|
Skubeka descendants. |
|
| |
|
|
|
La branche d'origine réglé par
Micah, déversement et de la douleur ŕ Cracovie. Rod inclus |
|
| |
|
|
|
entre les princes de Mazovie
(ksiac - kniežatko) jusqu'ŕ ce que Horodelskej Union. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Dans la période 1410
Jagellonne kráľVladislav et a entraîné son frčre Vitold - Lituanie |
|
| |
|
|
|
archiduc ŕ la guerre contre
l'Ordre Teutonique. Dans leur suite personnelle |
|
| |
|
|
|
un gardien a également été
Wezyk Jan Dabrowa dont transmis la langue allemande et |
|
| |
|
|
|
Mikołaj Wezyk i
Bogufał kuchmistri royale. membres de la famille ont été parmi
les |
|
| |
|
|
|
47 genres dans l'établissement
du veľkokniežatstva polka-Lituanie (Rzeczipospolitej |
|
| |
|
|
|
Obojga Narodowy)
10.02 1413 Horodle. Depuis lors, le «serment» genres |
|
| |
|
|
|
Horodelskej Union considéré
comme la plus haute noblesse polonaise et lituanienne, |
|
| |
|
|
|
qui sont aussi
appelés. prince (en Pologne et en Lituanie depuis le nedelila
noblesse |
|
| |
|
|
|
sur le classement) ŕ faire
preuve de respect pour les familles. Seuls les sous serment et les
familles de vote |
|
| |
|
|
|
élus pour l'archiduc. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci occupés dans les
étapes comme la plus haute fonction Vielopolski Duke, Duke |
|
| |
|
|
|
chasseur Koniecpolski, duc
Belsky, juge régional, commandant de l'armée, et Master |
|
| |
|
|
|
ci-dessous. Servi en tant
que maires et préfet TIC postes, la moelle épiničre, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Cracovie et autres Genre
également la résidence Château Kowal, Drahimia, Kornik et d'autres ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
Descendants des branches et
Kostrowicky Sulkovsky devenir grand prince |
|
| |
|
|
|
Lituanie et Ambrozievic tour
Lesser tchčque et le prince de Bohęme et de prince. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Družiníci Goriansky,
l'entourage royal accompagnent une princesse Anna, |
|
| |
|
|
|
qui sera publié sous le roi
Ladislas I de Hongrie, Saint, est devenu |
|
| |
|
|
|
magnat significative entre les
sexes de la Hongrie. Ils ont décidé que Bani en Slavonie, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Srem et MACV. Découlant
de ces deux branches sont membres Gorianskych |
|
| |
|
|
|
la famille se transforme
Uhorskými Palatin, oů le gouvernement a mené pratiquement au nom du |
|
| |
|
|
|
Le roi de Hongrie plus de 100
ans. Leur sičge principal ont été Devin Buda |
|
| |
|
|
|
et Siklos. Leur
appartenait et Liptovská comté, et Uhrovec Presbourg (Bratislava). |
|
| |
|
|
|
Principaux chiffres des
musulmans: John Venžík, qui est devenu |
|
| |
|
|
|
Hniezdenským archevęque et
primat de Pologne, aprčs la mort du roi |
|
| |
|
|
|
Vladislav a statué en vertu de
interegnum de jure Rex vice, jusqu'ŕ l'élection |
|
| |
|
|
|
New King .. Cette famille
a obtenu le privilčge de couronner les rois de Pologne, ainsi que |
|
| |
|
|
|
arrivé ŕ plusieurs reprises et
a reçu et d'autres privilčges importants. Comme primat de Pologne |
|
| |
|
|
|
a également eu un princes
séculiers rang Saint Empire romain germanique. La famille a été
plus |
|
| |
|
|
|
évęques, les prętres et les
princes. Mais seul l'Esprit, mais principalement gouverné par
l'épée |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci. Autre que John a
donné Venžík duc Podolsky cuisante défaite |
|
| |
|
|
|
Tatars. Comme preuve de
leur courage démontré par le fait que les cinq membres |
|
| |
|
|
|
famille a reçu la plus haute
décoration militaire Ordre Virtutti Militery. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Ce prix est considéré comme
l'un des trois najhonosnejších |
|
| |
|
|
|
Les grades militaires du
monde, ainsi que la Croix de Victoria et la Croix de la
Gloire. Autres |
|
| |
|
|
|
étaient en possession du
Conseil de l'Aigle blanc, et Saint-Laurent. George. Venžíci
que |
|
| |
|
|
|
commandants des troupes en vue
de faire respecter dehors de la Pologne et la Lituanie. O |
|
| |
|
|
|
les membres de la famille sont
en Pologne légende nationale plusieurs décrivant leurs |
|
| |
|
|
|
actes héroďques. Dans la
République tchčque a été le capitaine George Vladika Namest nad Oslavou |
|
| |
|
|
|
Jan capitaine Dionísius
Letovice, Jaros Hardeg autrichienne ŕ nouveau. Inclus |
|
| |
|
|
|
entre les défenseurs de la
fameuse Bible Kralice, qui a aussi grâce ŕ eux |
|
| |
|
|
|
a été préservé. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Sur le territoire de la
Slovaquie sont répertoriés depuis 1540. Stanislav Venžík |
|
| |
|
|
|
aux alentours de 1590, prit
pour femme Elizabeth Pograny baronne, sa fille |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kürt Baron Pograny Benoît
Nemes de. Il a participé aux batailles contre les |
|
| |
|
|
|
Turcs. Pograny était le
propriétaire et capitaine du château Viglas une activité anti- |
|
| |
|
|
|
des chasseurs turcs dans le
classement général de la Transdanubie. Ma fille est allée ŕ |
|
| |
|
|
|
commandants
najstatočnejších de son armée, et Stanislas Venchika |
|
| |
|
|
|
Comores Ladislas Zay
de. Stanislav Venžík tomba plus tard dans la bataille contre |
|
| |
|
|
|
Turcs autour de l'an 1595 dans
la bataille de New Castle. Depuis le mariage de |
|
| |
|
|
|
Baronne Elizabeth Pograny
tandis que son mari est devenu baron Ladislas Zay, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Zayovci ses descendants ont
fui vers le château lui-męme Uhrovec qu'ils avaient dans le |
|
| |
|
|
|
il appartient (ce mariage est
de nouveau réunis par le sang, avec une branche de Gorian). |
|
| |
|
|
|
Pas plus que les orphelins,
Zay est principalement préoccupés par leur propriété en particulier
Nemes |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kurth (ensembles Zemianske),
château et du manoir Viglas Bohunice en |
|
| |
|
|
|
qui ont été co-propriétaires
en proportion significative. Comment ne leur |
|
| |
|
|
|
Zayovci préparer la propriété
n'est pas entičrement connue. Probablement plus que |
|
| |
|
|
|
biens transférés orphelins
sous son administration. Depuis plus Venžíci |
|
| |
|
|
|
affectés ŕ des services
Zayovcov. Il ya lieu d'importantes fonctions économiques. |
|
| |
|
|
|
En 1659, le souverain restauré
statut aristocratique pour la Hongrie et l'ensemble Saint- |
|
| |
|
|
|
empire de Rome, une fois de
plus le mérite dans la lutte contre les Turcs. En 1675, le uvádzní |
|
| |
|
|
|
dans la noblesse d'inventaire
Bratislava selles. Mais combien peu riche famille |
|
| |
|
|
|
ont échoué dans tous les
postes importants. L'exception est Venchik Gaspar, |
|
| |
|
|
|
qui ont travaillé autour de
l'année 1845 en tant que juré sous serment Prešpor |
|
| |
|
|
|
selles. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Famille par le mariage du sang
est associée ŕ des souches de la Hongrie Zay de Comore, Balassa |
|
| |
|
|
|
Gyarmati de, Pograniy de Kurt
Nemes, Kohar Czabrak de, de Kalnoky |
|
| |
|
|
|
Kövöszpatak, Dobsa, Pongracz,
Vanko, Trebichavský, Babindali, "J, |
|
| |
|
|
|
Schur, les bouteilles,
meunier, Kušnier. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Aprčs 1804, ils sont passés de
Uhrovec et s'installe ŕ Trnava et ses environs. Vivre ici |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíci aujourd'hui. John
était aussi un membre de la brigade d'artillerie Wenžik |
|
| |
|
|
|
Trencin, qui a joué un rôle
important dans la mise en place de l'indépendance tchčque et |
|
| |
|
|
|
La Slovaquie aprčs la Premičre
Guerre mondiale. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Dans d'autres pays oů l'acte
est ŕ noter Venžíci significative |
|
| |
|
|
|
Počte français Guile Venzik
Kostrowicky - Apolinaire, qui a été |
|
| |
|
|
|
également un petit-fils de
Napoléon I. En outre, le savant tchčque et fondateur |
|
| |
|
|
|
Real tchčque Education Joseph
Wenzika (Wenzig), qui a également été |
|
| |
|
|
|
enseignants Chotkova Sophie,
épouse de l'héritier du trône d'Autriche-Hongrie, |
|
| |
|
|
|
ont été tués ŕ
Sarajevo. Son plus connus sont le livret de l' |
|
| |
|
|
|
crčme Libusa nouveau, Dalibor
et d'autres. Aprčs que Joseph est Wenzig |
|
| |
|
|
|
centre de la rue de Prague
nommé. Actuellement, l'Internet, on trouve |
|
| |
|
|
|
Venžíkov ŕ travers le
monde. Opérer ŕ partir du centre de données de la NASA, par le
biais |
|
| |
|
|
|
environnementalistes en
Amazonie, ou les médecins en Egipto, ou de gérer |
|
| |
|
|
|
groupe d'activités aux
Pays-Bas et la Russie dans la cour. Męme que Venžíkov |
|
| |
|
|
|
athlčtes dans les compétitions
internationales peuvent ętre trouvées, ou des étudiants universitaires |
|
| |
|
|
|
... |
|
| |
|
|
|
1. Mémoires
secrets: pour servir ŕ l'histoire de la république des ...: Volume 10 -
Page 322 |
|
| |
|
|
|
2. Dictionnaire
de la conversation et de la lecture: inventaire ...: Volume 14 -
Page 561 |
|
| |
|
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|
|
4. Atlantic
reporter: Volume 185 |
|
| |
|
|
|
5. Atlantic
reporter digest: covering all cases reported in Atlantic ...: Volume 6 |
|
| |
|
|
|
6. Les
Langues néo-latines: bulletin trimestriel de la Société des ...:
Numéros 208 ŕ 211 |
|
| |
|
|
|
7. Wolna szkoła polska w okupowanej Francji:
historia Gimnazjum i ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
8. Berlin!
Berlin!: ein literarischer Bilderbogen der letzten 150 Jahre |
|
| |
|
|
|
9. Nazwiska Pomorzan: pochodzenie i zmiany:
Volume 2 |
|
| |
|
|
|
. The first Slavic states, known through written sources, to be
inhabited by West Slavs were the Empire of Samo (623 - 658), the Principality of
Moravia (8th c. - 833), the Principality of Nitra (8th
c. - 833) and Great Moravia (833 - c. 907). The Sorbs and other Polabian Slavs likeObodrites |
|
| |
|
|
|
and Veleti came under direct Holy
Roman Empire domination after the Wendish Crusade[5] in the Middle Ages and had been strongly Germanized by Germans at the end of 19th
century. |
|
| |
|
|
|
The Polabian language survived
until the beginning of the 19th century in what is now the German state
of Lower Saxony.[6] To this day survived only 60.000
of Sorbs living predominantly in Lusatia, a region on the territory
of modern Germany in the states
of Brandenburg and Saxony.[7] |
|
| |
|
|
|
Historically, Western Slavs were also
called Wends (Venedi or Venedae in Jordanes and Tacitus).
Sometimes this term was limited to Western Slavic peoples living within
the Holy Roman Empire, though not always. Misico I, the first historical ruler of Poland, also appeared as Dagome, King of the Wends (Old Norse Vindakonungr). |
|
| |
|
|
|
eradicated heathenism, and founded the
bishoprics at Wrocław, Colberg, and Cracow, and an
archbishopric at Gniezno. Boleslav carried out successful wars
against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus and Lusatia,
and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a
tribute. Shortly before his death Boleslav became the first King
of Poland 1024. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Germaniae veteris typus (Old
Germany.),Aestui, Venedi, Gythones and Ingaevones on the right upper
corner of the map Edited by Willem and Joan Blaeu), 1645. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Wends (Old English: Winedas, Old Norse Vindr, German: Wenden, Winden, Danish: Vendere, Swedish: Vender) is a historic name for West
Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It
does not refer to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or
groups depending on where and when it is used. Today, it is used either in
historical contexts or as a catch-all term for Kashubians, Lusatian Sorbs, and their descendants, like
the Texas Wends. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Historically, Wends often referred
to Western Slavs living within the Holy Roman Empire, though
not always. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Mieszko I, the first historical prince of Poland, also
appeared as "Dagome,
King of the Wends" (Old
Norse: Vindakonungr). In Latin manuscripts (Jordanes, Pliny, Tacitus), Wends
or Venedi is
the designation for West Slavs, as opposed to Antes (East Slavs) and Sclavenes (South Slavs). The name has also survived in Finnic languages (Finnish: Venäjä, Estonian: Vene, Karelian: Veneä) denoting Russia.[1][2] |
|
| |
|
|
|
History |
|
| |
|
|
|
When Mieszko I (also Dagome)
inherited the ducal throne from his father he probably ruled over two-thirds
of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united
the Lechites east of theOder |
|
| |
|
|
|
(Polans, Masovians, Vistulans, Silesians) united into a single
country: Poland.
His son, Boleslav the Brave, with the assistance of Saint Adalbert, |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Teza nabierała popularności od początków państwowości polskiej w IX wieku. Gerhard z Augsburga w pisanej w latach 983 - 993 hagiografii świętego Ulryka (Miracula Sancti Oudalrici) niejednokrotnie nazwał Mieszka I wodzem Wandalów (dux Wandalorum, Misico nomine). Cytowany fragment dotyczył legendy, według której zraniony zatrutą strzałą władca uniknął śmierci dzięki pomocy biskupa Augsburgu, Ulryka. Był to pierwszy dowód jednoznacznie wskazujący na przodków dzisiejszychPolaków |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Sclavania igitur, amplissima Germaniae provintia,
a Winulis incolitur, qui olim dicti sum Wandali; decies maior
esse fertur nostra Saxonia, presertim si Boemiam et eos, qui trans Oddaram sunt, Polanos, quaia nec habitu nec lingua discrepant,
in
partem adiecreris Sclavaniae (łac. Słowiańszczyzna, największy z krajów germańskich, jest zamieszkana przez Winnilów, których dawniej zwano Wandalami. Jest to kraj przypuszczalnie większy nawet od naszej Saksonii; szczególnie jeżeli uwzględnimy w nim Czechów i Polan zza Odry, jako że nie różnią się te ludy ani obyczajem, ani językiem). |
|
| |
|
|
|
Niektórzy historycy sformułowanie Winnilowie uważają za zwykły błąd kronikarski, zaś domniemane wandalskie pochodzenie Słowian zachodnich za efekt pomyłki językowej (niem. Wenden - Słowianie; wyraz oparty niewątpliwie na łacińskim określeniu Venedi, jakim określano Wenedów).
W takim rozumieniu Wandalowie i Wenedowie mieliby być jednym plemieniem. Za taką argumentacją przemawia fakt, iż do około 1000 roku nie istniało jeszcze jednolite określenie na państwo Polan, a w większości publikacji starano się naśladować nazewnictwo rzymskie. |
|
| |
|
|
|
Louis Petit De Bachaumont, Mathieu Franois Pidanzat De Mairobert, Barthélemy-François-Joseph
Moufle d'Angerville - Afficher la publication entičre |
|
| |
|
|
|
Dans ce tableau historique de Wanclick , le monarque est accompagné du marquis
d'Haruilton , son premier écuyer ; il a derričre lui un page , fils de
ce seigneur , qui porte le manteau do sa majesté Britannique. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
William Duckett - 1857 - Afficher la publication entičre |
|
| |
|
|
|
est d'une couleur Wanclic; l'épiderme. est cendre, tout M qui est derme est blanc. «
le pigmentuin n'est quVae, simple codeh«, un enduit, un
dépôt, ajoate M.iF4o«en«, et non une membrane.
La membrankqaileireooiurce est, une ď çii- lahle... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
1997 - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
This kinematic formulation has been developed
by Aitchison and Wanclik [1] and Mukunda and Simon [2]. Hilbert space
being centra] to standard quantum theory, the quantum geometric phase
has great relevance. From the kinematic approach,... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
West Publishing Company -
1936 - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
Wanclik 256 Horowitz v.
Beamish 760 Hortman, Appeal of 740 Horvat, In re
266 Ilostetler v. Kniseley 300 House v. Brant 628
Hubbard, Dobrowolski v 061 Hudson & MRR, Gross v
365 Huester. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
West Publishing Company -
1957 - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
... it could reasonably
be inferred that third party was agent of defendant in collecting claim, and
not an independent contractor. Pub.Laws 1935, c. 2190, § 45.— Wanclik v. Franklin Auto
Supply Co., 10 A.2d 349, 64 RI 76. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
Société
des langues néo-latines - 1974 - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
... langues néo-latines UER DE
LETTRES et SCIENCES HUMAINES INSTITUT D'ESPAGNOL Mont Saint Aignan, le 8
février 1974 Sont présents : Mlles DECORTE, GRENET, RATHONIE Mmes ROIGEY,
CARPENTIER, EDELIN, SEQUERRA, VA- LENTIN, 'WANCLICK MM. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
Tadeusz Łepkowski -
1990 - 321 pages - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
Wanclik Elżbieta, 13 II 1930,
Cagnas-les-Mines (Tarn); II - IV g. 1943 - 44, 1944 - 45 i 1945 -
46. Wandycz Piotr, 20 IV 1923, Kraków; II 1. 1940 -
41. Wawak Helena, 6 XII
1922, Moravska Ostrava (Czechosłowacja); I-II
1. mf (I 1. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Ajouter
ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
Gustav Sichelschmidt -
1980 - 212 pages - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
Marne, an der Somme, am Chemin des
Dames, vielleicht im Kampf gegen tschechische Legionäre,
die Mares, der Sponar, der Wanclik . .
. Das sind Namen, denen man überall begegnet zwischen alten deutschen, manchmal ist auf Flimmerschildern ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Ajouter
ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
Edward Breza -
2000 - Extraits |
|
| |
|
|
|
... i Wencel oraz Wancel 49,
z tego 26 w woj. zielonogórskim,
12 opolskim, por. też Wancław 20: 12
w woj. gdańskim, 7 zielonogórskim,
1 wrocławskim i pochodne Wanclik 23: 4 w woj. słupskim,
10 katowickim, 6 wrocławskim, 3 legnickim. ... |
|
| |
|
|
|
books.google.fr - Autres éditions - Ajouter ŕ Ma bibliothčque▼ |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
http://wiedza.free.fr/geschichte-boehmens/index.htm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|




